
Agriculture
November 9, 2023
AguaClara Reach PF 300
Read SolutionImplemented by
Agua Clara LLC

Updated on November 9, 2023
·Created on September 10, 2020
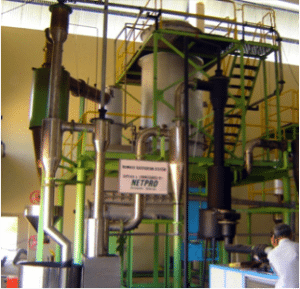
AguaClara Reach Full Scale Plant is a gravity-fed water filtration system.
The AguaClara Reach Full Scale Plant is a compact gravity-fed water treatment system that uses a five-step process to treat and filter water for 1,000 up to 50,000 people.
Target Countries
Honduras, India, Nicaragua
Target SDGs
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
Market Suggested Retail Price
$233,453.00
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Community
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
This product is implemented and distributed by Cornell University and Agua Clara LLC
Competitive Landscape
Direct competitors include GravityPure UF.
Manufacturing/Building Method
The product is produced within the community using local materials.
Intellectural Property Type
Open Source
User Provision Model
This product is distributed by Cornell University Engineering Department
Distributions to Date Status
20 plants built in Honduras, reaching 77,000 people 7 plants built in India, reaching 2500 people
Design Specifications
The AguaClara Full Scale Plant removes large sediment and grit before introducing coagulant and chlorine through a chemical dosing process. After this, the water begins a flocculation and sedimentation process where the sediment and particulate matter is collected in a flock blanket and disposed of as waste. The residual water passes through angled plates and enters a six-layered Stacked Rapid Sand filter. The effluent water is collected in a distribution tank for use.
Technical Support
Provided by the manufacturer
Replacement Components
N/A
Lifecycle
Unknown
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
<0.3 NTU effluent turbidity
Vetted Performance Status
0.3 NTU effluent turbidity
Safety
Provided by the manufacturer
Complementary Technical Systems
None
Academic Research and References
Chavez, K., 2013, Introducing AguaClara: The Process of Establishing a Pilot Plant in the State of Chiapas, Cornell Institute of Public Affairs.
Kelley, C., Krolick, A., Brunner, L., Burklund, A., Kahn, D., Ball, W., Weber-Shirk, M., 2014, An Affordable Open-Source Turbidimeter, Sensors 14(4), pp. 7142-7155.
Adelman, M. et al., 2013, Floc Roll-up and its Implications for the Spacing of Inclined Settling Devices, Environmental Engineering Science, 30(6).
Adelman, M. et al., 2013, A novel fluidic control system for stacked rapid sand filters, Journal of Environmental Engineering.
Swetland, K., 2012, From stock to floc: an investigation into the physical/chemical processes controlling aluminum sulfate and polyaluminum chloride behavior in a gravity powered drinking water treatment plant, Cornell University.
Swetland, K. et al., 2012, Predictive performance model for hydraulic flocculator design with polyaluminum chloride and aluminum sulfate coagulants, Journal of Environmental Engineering.
Compliance with regulations
Effluent turbidity is in compliance with the WHO standard of <5 NTU turbidity.
Evaluation methods
Unknown
Other Information
None

Agriculture
November 9, 2023
Implemented by
Agua Clara LLC

Agriculture
November 9, 2023

Agriculture
November 9, 2023

Agriculture
November 9, 2023

Agriculture
November 9, 2023

Agriculture
November 9, 2023
Agriculture
November 9, 2023

Agriculture
November 9, 2023

Agriculture
November 9, 2023

Agriculture
November 9, 2023
Implemented by
Bici tech
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback