
Agriculture
November 9, 2023
Updated on November 9, 2023
·Created on September 1, 2021
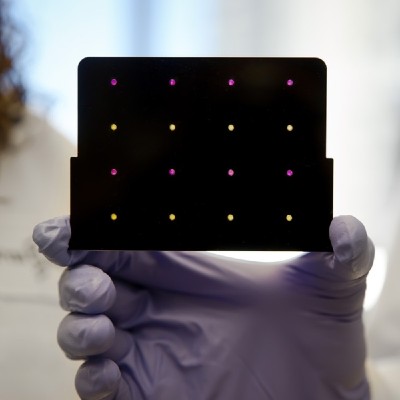
A paper-based diagnostic device to detect viral threats
A Zika paper-based diagnostic device is a molecular diagnostic tool embedded into paper that uses blood, urine or saliva to provide results in a short time. It is composed of three components: An amplifier for the genetic sequences found in the patient sample; a toehold switch sensor to recognize if the sequences found are from Zika virus, and a third component to determine the strain of the virus. This product is still a proof of concept, and additional testing is needed to ensure safety and efficacy before actual deployment.
Market Suggested Retail Price
$1.00
Target Users (Target Impact Group)
Distributors / Implementing Organizations
Unknown
Manufacturing/Building Method
This device takes approximately 5 days to be manufactured at the synthetic biology laboratories from the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering.
Intellectural Property Type
Patent Protected
User Provision Model
Product not commercially available yet.
Distributions to Date Status
None
Design Specifications
Following the World Health Organization (WHO) criteria for rapid diagnostic tests, researchers aimed to create a sterile and abiotic platform that can be utilized outside of laboratory conditions without concern over biosafety. Requirements:
Technical Support
Provided by manufacturer.
Replacement Components
N/A
Lifecycle
Single use, disposable test. 1 year in storage.
Manufacturer Specified Performance Parameters
Testing time is less than 3 hours. The amplification and DNA detection process uses a NASBA (nucleic acid sequence based amplification) due to its high sensitivity. The chance for false-positive results due to contamination are minimized by the use of sequence-specific toehold switch sensors and CRISPR/ Cas9-mediated selection downstream of the amplification. This paper-based test is able to detect 2.8 fM Zika concentrations in plasma samples, which make it clinically relevant. It is fast, easy-to-use, and requires no costly qPCR machine and PCR infrastructure, no cold-chain required. Only needs an electronic optical reader, which was also designed for low resource settings.
Vetted Performance Status
Tests were performed by the manufacturer, collecting samples from three Latin American countries: Ecuador, Brazil and Colombia.The device showed high specificity against similar regional viruses (Dengue and Chikungunya), similar sensitivity when compared to RT-qPCR for the Zika detection, and a diagnostic accuracy of 98.5% with 268 patient samples.
Safety
Additional testing would be needed to ensure safety and efficacity before actual deployment of this device.
Complementary Technical Systems
Academic Research and References
Pardee K., 2016, “Rapid, Low-Cost Detection of Zika Virus Using Programmable Biomolecular Components,” Cell, 165 (5), pp. 1255-1266
Hall R., Macdonald J., 2016, “Synthetic Biology Provides a Toehold in the Fight against Zika,” Cell Host & Microbe, 19(6), pp. 752-754,
Silva SJRD., Pardee K., Pena L., 2019, “Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) for the Diagnosis of Zika Virus: A Review,” Viruses,12(1):19.
da Silva, S.J.R., Pardee, K., Balasuriya, U.B.R. et al., 2021, “Development and validation of a one-step reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) for rapid detection of ZIKV in patient samples from Brazil,” Sci Rep, 11, pp. 4111
Karlikow, M., Silva, S. J. R. D., Guo, Y., Pardee, K., 2021, Developing a lab-in-a-box and low-cost paper-based sensors for ZIKV and CHIKV diagnosis in Latin America. V International Symposium of Immunologicals.
Silva, S. J. R. D., Mendes, R. P. G., Pena, L., 2021, Low-cost protocol for rapid detection of ZIKV from patient and mosquito samples using a direct-RT-qPCR assay without RNA extraction step. V International Symposium of Immunologicals.
Compliance with regulations
Unknown
Other Information
Similar applications of this diagnostic platform have been made for Chikungunya and COVID-19 by the same researcher.

Agriculture
November 9, 2023

Agriculture
November 9, 2023

Agriculture
November 9, 2023
Agriculture
November 9, 2023
Agriculture
November 9, 2023

Agriculture
November 9, 2023

Agriculture
November 9, 2023

Agriculture
November 9, 2023

Agriculture
November 9, 2023

Agriculture
November 9, 2023
Implemented by
Nanyang Technological University (NTU) Singapore
Have thoughts on how we can improve?
Give Us Feedback